The Complete Guide To Improving Technical SEO Of A WordPress Website (For 2024)

So, you are looking for ways to improve your website’s technical SEO or you might be trying to fix technical errors on your website with a technical SEO audit. You might be missing out on traffic, wondering if your website’s technical health is good and want to do a site audit for technical SEO.
As we venture into 2024, ensuring your WordPress site is technically optimised for search engines has never been more pivotal for standing out in SEO space. This detailed guide is crafted to assist you in navigating the intricacies of technical SEO this year, making certain your website is primed for both search engine recognition and user engagement.
From improving site speed and ensuring mobile-friendliness to implementing structured data and more, we delve into all the vital optimisations essential for enhancing your website’s visibility and performance in 2024. Whether you’re refining an existing platform or embarking on a new website project, this guide offers the expertise and actionable advice to advance your WordPress site’s SEO standing.
If your site and pages can not be seen, indexed, crawled and ranked on the first page of SERP, there’s not much return to business value you can expect from your website. This is precisely where technical SEO audit and optimisation come into play.
Fairly speaking, technical SEO fixes are not easy to implement but with this guide, we’ll go through how you can perform a technical SEO audit of your website and the ways to fix the issues while following best practices.
Table of Contents
- What is Technical SEO?
- How do technical SEO factors contribute to search engine rankings?
- Technical SEO Audit
- Step-by-Step Technical SEO Checklist
- Tools For Technical SEO Audit & Fixes
- FAQs
What is Technical SEO?

Technical SEO is a part of SEO that focuses on improving your technical aspects to ensure that your website can be indexed & crawled by search engines and finally, display your webpage when relevant intent keywords are searched for in the search. All in all, technical SEO Audits ultimately help search engines to understand our website better, and improve search rankings & organic traffic while also providing a better website page experience.
Finding out technical issues and fixing them does involve a lot of work. Especially, when you are unsure of the issues or when you are a beginner. This includes everything from optimizing website loading speed and performance, ensuring the site is mobile-friendly and responsive, implementing XML sitemaps, data & schema, and site architecture optimisations, and creating WordPress redirects and canonical tags.
We use various tools and techniques to discover and fix the issues around the technical aspects of websites like AHREFS, Google Analytics or Search Console, Yoast, RankMath and WordPress Redirect plugins. Some of these fixes might require the attention of a website developer while some of them can be done by non-technical people like you and me.
How do technical SEO factors contribute to search engine rankings?
Technical optimisations are done for improving search engines’ understanding of a website’s content and context, resulting in higher ranks. Let’s take an example of site speed as an important SEO ranking factor. If a site speed is faster, it generally improves user experience, resulting in reduced bounce rates and increased engagement. You can see this yourself by comparing the average session duration in Google Analytics.
To improve page loading speed, you might want to reduce the size of images, try and decrease the overall page size, delete or optimise existing CSS and JavaScript files, cache at different levels and do other optimisations that would contribute to a faster web page.
Factors like mobile-friendliness, responsiveness, structured data and website structure are other major technical SEO factors that influence search rankings. The vast majority of search queries come from mobile users and no wonder, search engines prefer websites that are mobile-friendly and responsive.
Using responsive web design, optimising photos, and employing proper font sizes help you with mobile version optimisation. You need to make mobile users a priority and optimise your website for these visitors by making the mobile version of your site available.
Mobile-friendly optimisations result in a better page experience, increased engagement, and fewer bounce rates, all of which can improve a website’s rank in search results. Using HTTPS pages ensures that your website is secure and follows certain standard guidelines.
Similarly, there are other factors that also provide a measure of your overall site performance and help the search engines to understand your website and determine your rank on the results page.
Technical SEO Audit
Performing Technical SEO audits and fixing website issues is my first step in starting an SEO project. It helps to set the foundations for Search Engine Optimisation before I jump onto any other optimisations such as on-page SEO optimisations or internal and external links.
Technical SEO audit is essential to find out areas of improvement to your website. There are plenty of SEO tools that can perform the site audit to find out the issues. Tools like AHREFS are actually good at figuring out the issues, it’ll give you a list of SEO errors and suggestions to improve along with the priorities for each error.
But you can not expect a tool to figure out all of the Technical issues and factors involved. So, you need to know quite a few things before you jump into finding technical areas of improvement for SEO which we’ll discuss below.
Technical SEO Audits and fixes are not definite and optimisations certainly can vary depending on the websites. But there are areas where you can look to find the issues or potential improvements. While starting with technical audits, these are some of the factors you can look into to make the most out of your SEO efforts.
Website Structure, Navigation and URLs
Google and other search engines need to crawl and index your website while also determining its relevancy. So, the structure and navigation of a website are significant factors for SEO. Start with analysing the website structure and navigation in a technical SEO audit to find if there are any issues such as broken links, identify duplicate pages, missing pages, or redirect chains.
HTTP status code is considered less secure so, if there are any HTTP pages, you might want to remove or redirect them to HTTPS pages. It is important to classify the pages as category pages, sub-categories and product pages.
Also, check if the website can be easily navigated and is optimised for both search bots and people. If there are any links that are not working consider removing or updating them. You can also provide canonical or redirect the web pages as necessary to fix navigation issues.
On-Page SEO Technical Check
On-page SEO focuses on improving individual web pages in order to rank higher in organic search results. While on-page technical SEO audit is reviewing keyword research, title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, and keywords are in place and performing well.
Website Speed and Performance
Website speed is now more crucial than ever as no one likes to visit a website that loads slowly. Search engines want their users to visit a website that provides a seamless user experience and thus, site speed is also an important factor for your site’s SEO success.
You can analyse the website’s speed and performance with measures such as poor loading times, big image sizes, or render-blocking JavaScript. Tools like Page Speed Insights and GTMetrix are some tools that will give you an insight into your site speed and overall performance.
Mobile Optimisation
With the maximum number of users coming from mobile, it only makes sense to see if your website performs well in mobile formats and devices. You can see your percentage of mobile users by navigating into Google Analytics.
It is important to assess if the website is responsive as well as mobile-friendly. You should check that your site is responsive and easy to use on portable devices.
Check if your website is optimised for mobile by using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test Tool.
These are some of the areas where you should be focusing on for SEO technical analysis. By considering the factors above, you as a website owner or an SEO professional can identify and solve the technical SEO issues.
Configuring these aspects properly can positively impact a website’s SERP rankings, leading to improved visibility and better user experience. Now that we know the whereabouts of Technical optimisations, let’s get started with step by step Technical SEO Audit checklist.
Step-by-Step Technical SEO Checklist
Technical SEO Audit is only about half of the job here. While the audit helps you find out the issues and figure out SEO strategies, there still remains the task to fix those issues. Below I’ll discuss more on the actual steps and processes you need to do in order to find if there are any misconfigurations and to fix the issues.
I have assumed that you already have set up your Google Search Console, Google Analytics and some other SEO audit tools you might need actually to get to work on these technical fixes.
Website Indexing
If your website is crawled by Google, has been analysed for content and is stored on Google index, it is said to be indexed. And, how do you check if it’s indexed? Simply perform a site search on Google.
Go to Google Search, type “site:yourwebsite.com” and search. Replace ‘yourwebsite.com’ with your actual website name. This will display all of your Google-indexed web pages on your website.

Similarly, if you want to check for a specific URL, replace ‘yourwebsite.com’ with the URL of the web page or blog posts you want to check to index. For example, site:yourwebsite.com/blog/technical-SEO/.
Sitemap
Sitemaps are simply the list of all the web pages in XML or HTML format, used by search engines to determine information about all the pages on your website. You can use different tools like Yoast SEO, and Screaming Frog to create a sitemap. Or, you may also create a sitemap on your own.
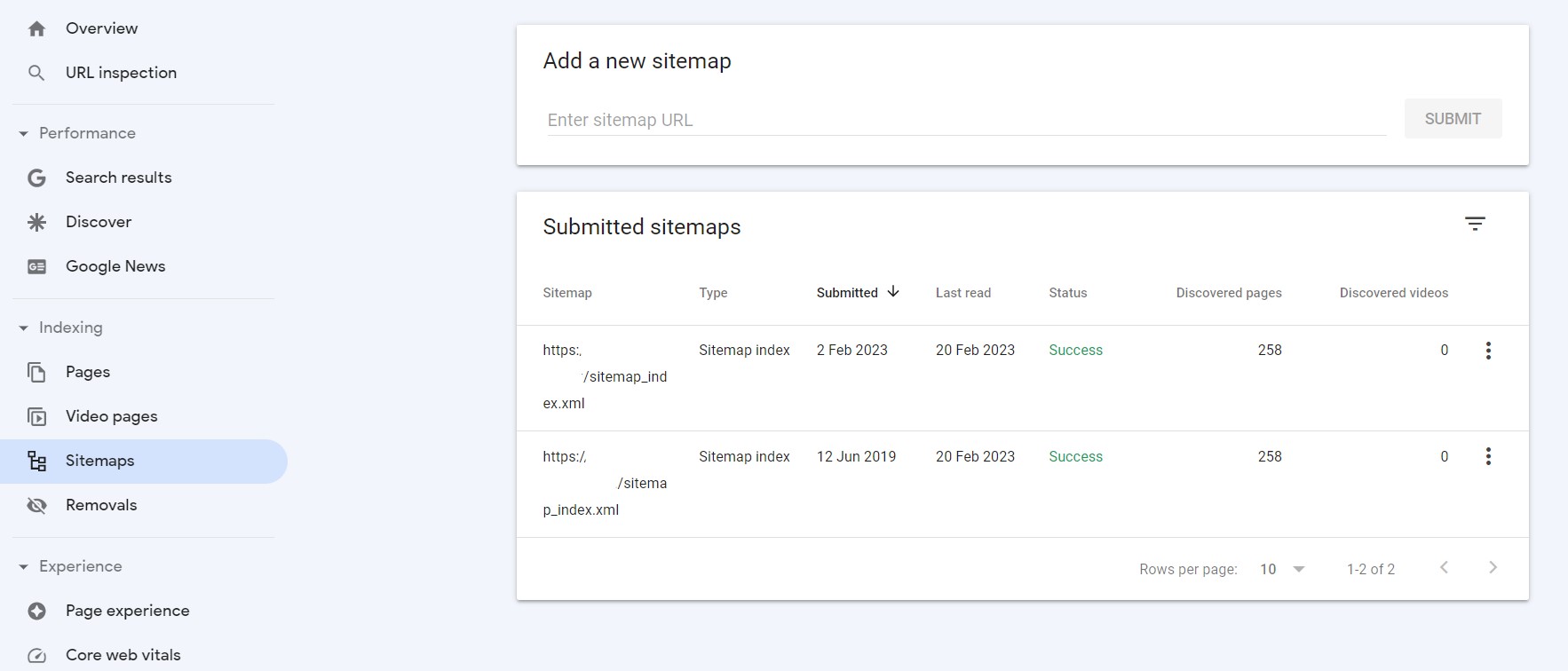
You need to upload a sitemap in Google Search Console. Upload the sitemap to the server and submit the URL in Google Search Console. If you have WordPress SEO plugins installed on your website, they may also have a feature to add & submit a sitemap.
Check if your sitemap is up to date and includes all of your pages. You can use tools like Google Search Console to review your sitemap or you can also view it manually from the URL or by downloading it.
Crawl Errors
Look for any crawl errors or broken links that could prevent search engines from accessing your site’s pages. You can use tools like Google Search Console, AHREFS or Screaming Frog to check for these errors. I use ScreamingFrog to check any crawl errors and URL issues. It does the work for most technical URL issues and fixes.
URL Structure And Site Architecture
The URL structure of your website should be clear and descriptive, using standard naming conventions to help search engines understand the content of each page. You should check for issues such as lengthy, dynamic URLs or those containing parameters that can confuse crawlers.
One of the best ways to figure out complex URLs is by downloading an excel version of your website URLs with Search Console or Google Analytics and using filters. You need to exclude or delete the pages you don’t need anymore or are outdated which also helps you to manage Google’s crawl budget.
Cleaning up your site structure can help search engines to understand your website and rank for the keywords your webpage is relevant to.
Use clear paths & URLs, and implement proper hierarchy within the site and make it easier to navigate. For example, use clear paths like ‘yourwebsite.com/services/service-page’ for service pages.
Clean up your site by using Google Analytics to find the pages with no sessions & visits in the past 3 months, and deleting and/or redirecting them as necessary.
Page speed and performance
Page speed is an important ranking factor, so make sure your site’s pages load quickly. You can use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to check your site’s page speed.
Core Web Vitals are performance indicators and page experience signals introduced by Google in May 2021, that assess a website’s user experience. Site speed and visual stability are among these measures. The core web vials are the ranking factors for Google’s search algorithm to offer a better user experience. So, you must optimise your website for Core Web Vitals.
You can do this in several ways. To start with, go to Google Page Speed Insights Tool and enter your website’s URL to start the test. Then, the tool will score your websites based on different factors and also lets you know the areas of improvement including core web vitals optimisations for a better score.
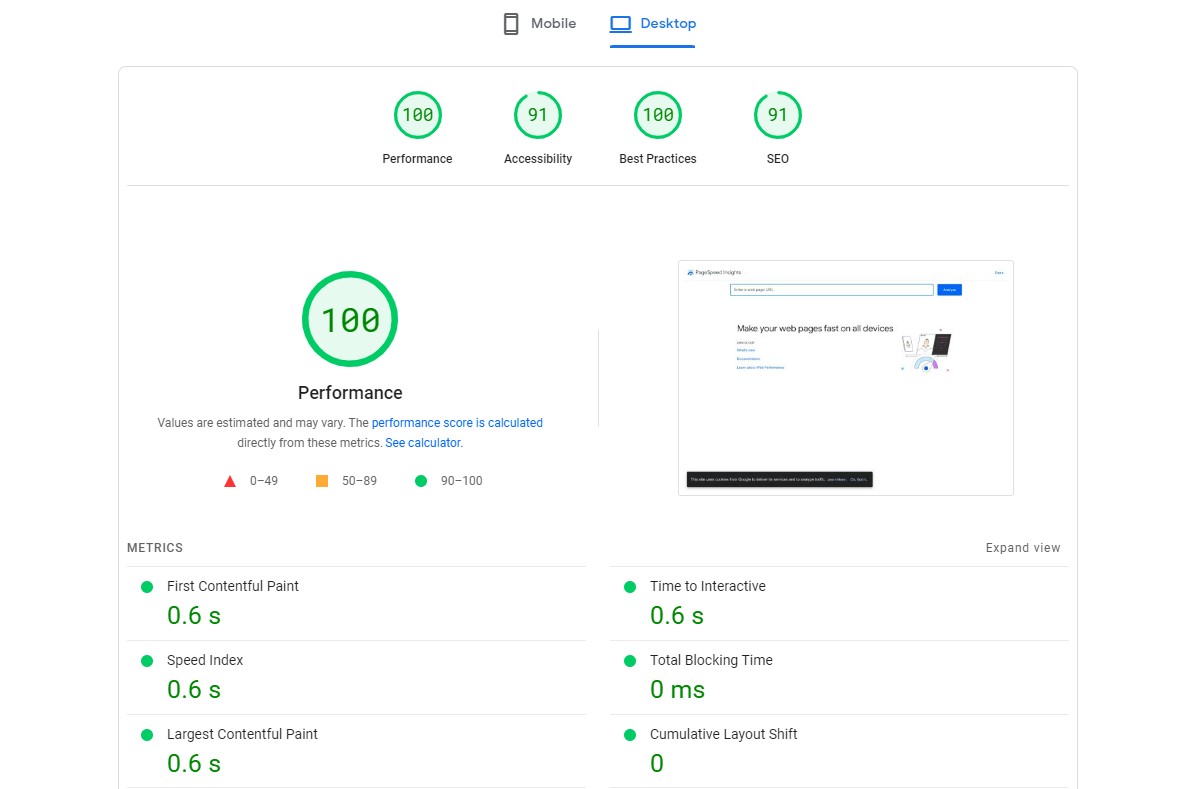
You can improve the loading speed of their website by using a content delivery network (CDN), optimizing images, compressing files, and minimizing HTTP requests. Improve interactivity by reducing the time it takes for users to interact with the website by using plugins for cache, minifying code and optimising images.
Finally, you can improve visual stability by reducing layout shifts, which occur when elements on the page move unexpectedly by setting sizes for images and videos, avoiding dynamic content, and using CSS for layout. These should help in improving Google’s page experience signals or the Core Web Vitals score of your website.
Mobile-Friendliness
As more people use mobile devices to browse the web, it’s essential to ensure your site is optimized for mobile and tablets. You can use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check if your site is mobile-friendly. Go to the Google Mobile-Friendly Test Tool, enter your website and you will get the report on any issues.
Another way to check for mobile friendliness on your site is by conducting a manual review. Visit your web page on your mobile device or you may also use an emulator. Then, check if anything is unresponsive, navigation issues, image and font sizes. You can ask other people to use the website on their phones and ask for feedback to improve the mobile user experience.
The search console also reports errors and issues regarding mobile usability.
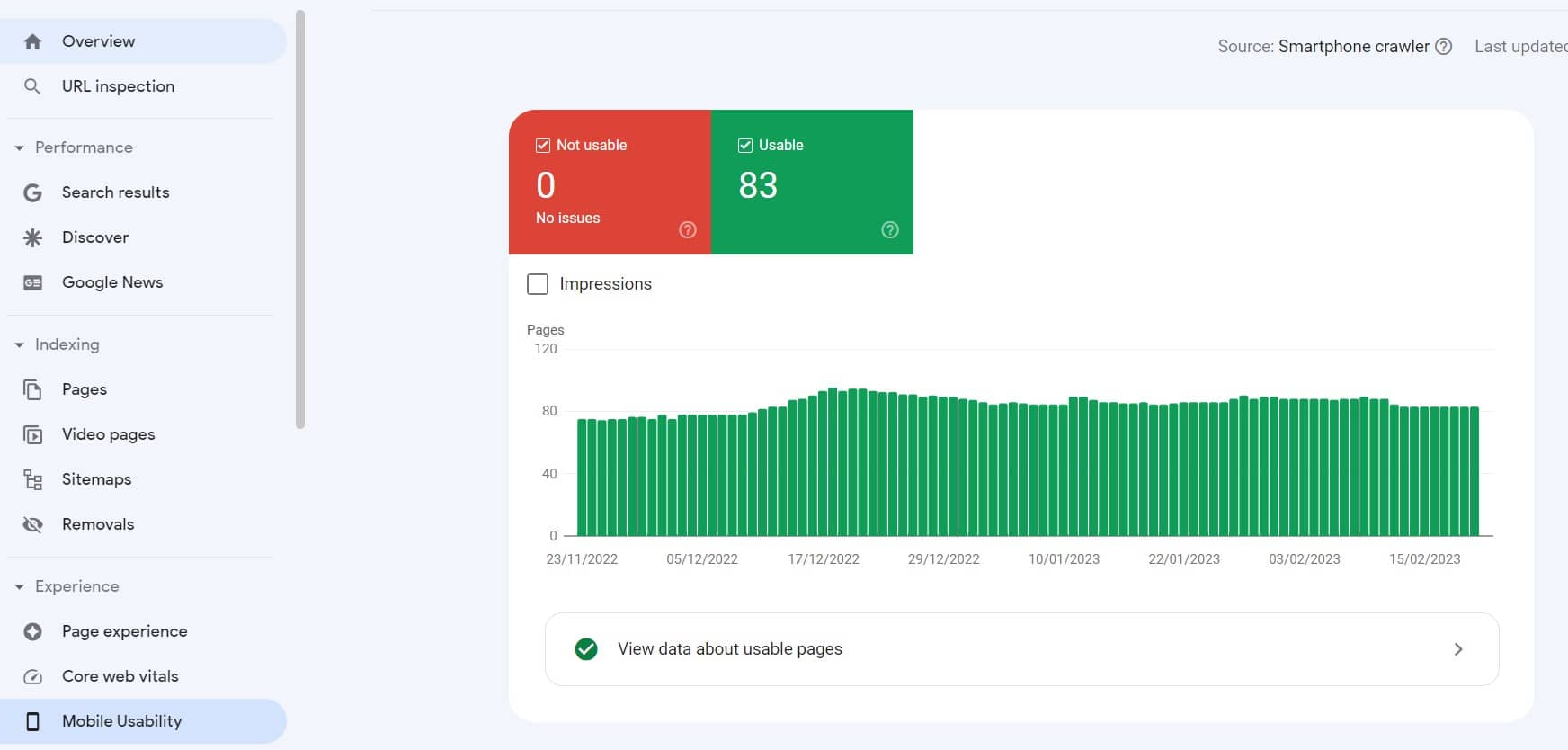
Also, consider reviewing website usage and sessions of mobile users in Google Analytics to see further improvements.
Internal Linking
Make sure your site’s internal linking is optimised to provide a good user experience and help search engines understand your site structure. Internal links are links on your website that go to other pages on the same site.
The purpose of these links is to make your website user-friendly, ensure page accessibility and link relevant web content. You can use tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to find out details of your internal links.
If the links are broken, fix the links or use redirects. Check if the anchor texts are relevant and are used as necessary. Add links to every relevant page, unless you do not want Google & users to see the page.

Apart from these, you can also review if any links are buried in the menus and are difficult for users to find. Linking the pages in your website properly helps to pass the link juice and ultimately improve SEO.
Another thing you might want to look at is the link profile audit and the ratio of external links to internal links. Try to use more high-value links (high DA, search traffic and relevancy) as much as possible.
The number of links coming to the page should not be super imbalanced. For example, if the number of internal links pointing to a page is 100 you might want to keep external links pointing to the page to around 100, not 1 or 1000.
Schema Markup & Rich Results For Search Engines
Adding schema markup to your site’s pages can help web search engines, as well as the users, understand the content of your pages and what your page is really about. Make sure your site has appropriate structured data where applicable.
Check if your page supports rich results with Google Rich Results Test Tool.
The rich data assists Google and users in better understanding your website content. This includes the type of page content, the author, the date of release, reviews, price and much more. Rich results include star ratings, reviews, prices, and other information. This helps you appear in rich results which can boost your site’s exposure in search results and raise your click-through rates.
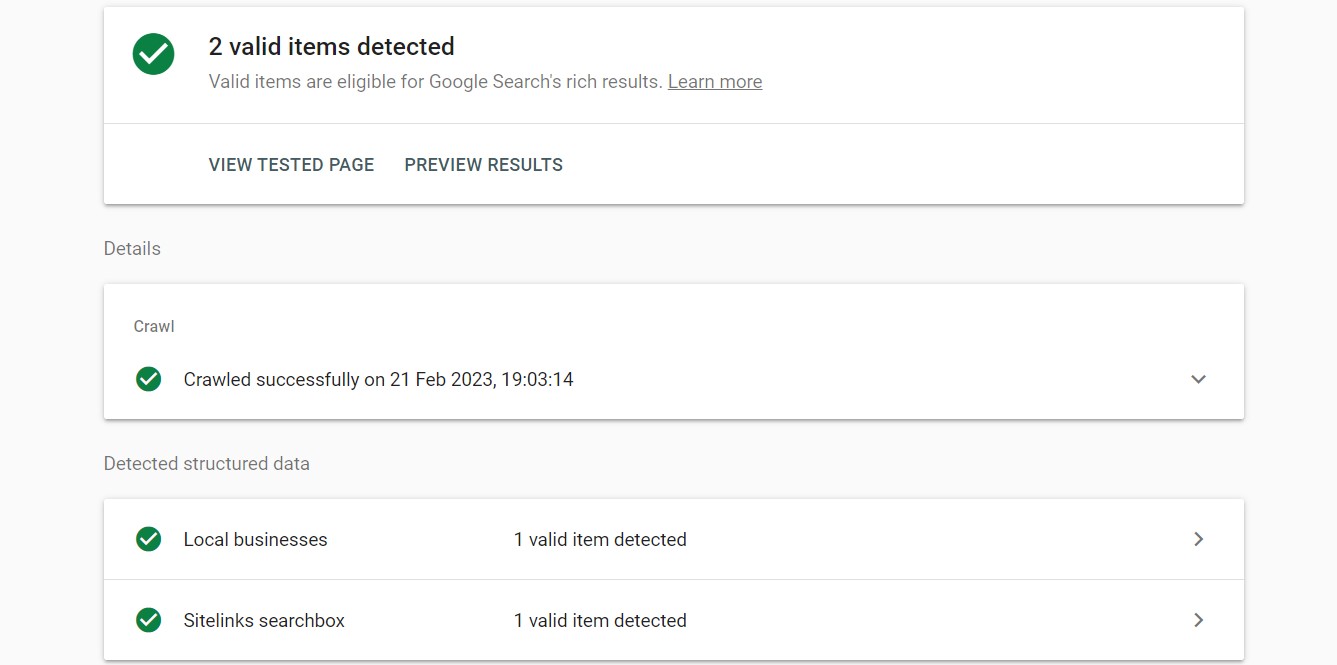
Schema markup can be implemented in different ways. You can either use a plugin/tool to generate the structured data or create them annually by writing code. If you are using a tool or a plugin, you need to specify the type of page and other descriptions. Visit Schema.org for more information on using and creating schemas.
Review Google Search Console And Bing Webmaster Tools
Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster tools can not be missed while performing technical SEO. These two are the free tools developed by Google & Bing themselves and they surely have got a bunch of features that are guaranteed to help you if you are looking to enhance your digital marketing and SEO efforts.
You need to first set up your Google Search Console for your website. Sign up for Search Console and verify your website to get started.
Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools can help you identify crawl errors, broken links, and any other issues that may be affecting the visibility of your site in Google search results. It has the capability to submit XML sitemaps, test and submit specific URLs for crawling, and even see which pages of your site are presently indexed by Google.
Make sure to check for any tech issues that are reported on Google Search Console. It gives insights into technical errors that might be negatively affecting your SEO including indexing, duplicate pages, security, and canonical issues.
Robots.txt
To start with, place the file in your website’s root directory and this is where search engine crawlers will check initially for the file. You can use the robots.txt file to tell search engine crawlers which pages and portions of your website to crawl and index, and which to ignore.
For instance, you might use robots.txt to exclude sites with duplicate pages or low-quality content or to prohibit Google from crawling pages with sensitive or private information. You may also use robots meta tags to block search crawlers from indexing areas of your site that aren’t as significant or relevant to your target audience.
For example, if you want to block the page ‘abc.com/user-info’ using robots.txt, you would add the following code to the file:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /user-info
While robots.txt may help to control how search engine bots scan and index your website, some crawlers may disregard the instructions in the robots.txt file and some may misinterpret them. For this, try to align robots.txt with other technical SEO aspects such as meta tags, canonical tags, and XML sitemap.
Duplicate Content
Search crawlers find duplicate content confusing and it has been one of the most common SEO mistakes which lead to poor organic performance. Duplicate content can affect your site’s search rankings, so be sure your site doesn’t include any.
Identify Duplicate Content
Here are some pointers on how to identify and resolve duplicate content issues:
Use free and commercial duplicate content chequer tools accessible online to assist you to identify duplicate content issues on your website. These tools will search your website for similar or identical pages or content and report it.
Making use of Canonical tags to inform search engines about the main or original version of a page is another way to fix duplicate content issues. You will also need to check your website’s canonical tags to ensure that they are correctly pointing to the primary version of each page.
If you have multiple versions of a page or content on your website, use 301 redirects to redirect traffic to the main version of the page. This will help the crawler identify the primary version of the page and avoid any confusion. You should consider merging contents into a single page if multiple pages have similar content.
Rewrite your content if you think duplicate content can not be merged, canonical tags can not be used and redirects are irrelevant. Rewriting is the best way to make the content unique and fix the duplicate content issue. This is the best way but I know it takes time and effort. But, it can help to improve your SEO performance and provide more value to your users.
You should ensure that you have the appropriate analytics and tracking tools to monitor your website’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
By following these steps, you can perform a comprehensive technical SEO audit of your website and identify any issues that may be impacting your organic rankings. You might also want to consider checking in Google Analytics, Search Console and other SEO tools.
Tools For Technical SEO Audit & Fixes
Screaming Frog
ScreamingFrog is a great tool for scanning websites to find out technical issues. It is simple to use but powerful and can assist you in analysing a site structure and identifying technical faults that may be causing your website to fall behind in search engine results.
Screaming Frog can create XML Sitemaps and is available for free in the lite edition for up to 500 URLs. Anchor texts, indexability, title tags, H1 and H2 use, word count, file size, and other SEO insights are also provided by the tool. But, it is mainly used for checking links, URLs and site structure.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console identifies and reports technical matters that may be affecting your site’s visibility in SERP. It also gives you insights into how Google crawls and indexes your site. But, Google Search Console is not only important for technical. It is a must-have tool for every website owner or SEO professional wanting to enhance their website’s SEO of their site.
Similar to Google Analytics, it is can be used to view organic search performance on Google. It can also sometimes serve as a bridge between Google Search Engine and your website as you can submit XML sitemaps, request indexing, and find reports on manual guidelines and security actions.
Google Page Speed Insights
PageSpeed Insights by Google assesses your website’s loading speed and makes recommendations for enhancing its performance. It will score your site speed and performance and help you in identifying technical issues that may be slowing down your website.
Related Read: How to Score Perfectly on Google Page Speed Insights Test Tool?
Google Mobile Friendly Testing Tool
Google Mobile Friendly Testing Tool tool assesses how well your website performs & the website UX on mobile devices and makes recommendations for mobile optimisation.
Google Structured Data Testing
Google Structured Data Schema Testing tool allows you to test and validate the schema code snippet and rich results on your website. This ensures that Google understands and shows the material appropriately in search results.
AHREFS
AHREFs is a great SEO tool for all-around optimisations including monitoring & building your website’s backlink profile, tracking keyword ranks, content marketing, and identifying technologies that may be influencing your site’s search rankings. It is also a great tool to audit your website’s SEO audit tool and allows you to compare site metrics over time.
AHREFS also offers a site audit feature that specifically scans your entire website for technical errors, tracks tech issues and also fixes them. It is mostly famous for its backlinks checker tool which can help you with your link-building campaign.
Chrome Web Developer Tools
This is mostly used by coders and is available in the Google Chrome browser (Press Ctrl+Shift+Iin Google Chrome). It can assist you in debugging and optimising the code of your website. You can inspect and edit HTML and CSS, measure website load speeds, and simulate mobile devices.
App JSON-LD Generator
App JSON-LD Generator assists you in creating JSON-LD structured data for your website’s mobile app. This allows search engines to better understand your web page and show information about your website in search results.
Hreflang Tags Tester
This HrefLang testing tool analyses your website’s hreflang tags to ensure that they are appropriately set up, allowing search engines to display the right version of your website to people in different countries or languages.
Redirect Path Plugin
The redirect path plugin is for anyone who would like to implement redirects easily on their website without much technical knowledge.
These are only some of the plugins that will help you with Technical SEO audits and fixes. And, there are many more like Yoast, RankMath, Google Analytics and SEMRush that directly or indirectly contribute to technical SEO.
Looking for SEO experts to manage technical optimisations for your website? We are the most trusted SEO agency in Sydney.
FAQs
What is a technical SEO audit?
Technical SEO audit is the process of reviewing, analysing and finding out technical issues aspects of a website that affects the visibility of the website in the search engine results page. Technical SEO factors are the basic foundations for SEO to find your website and they are extremely important for a website’s organic performance on search engine results pages. Advanced ranking algorithms are used by search engines to rank websites by considering factors like relevancy, authority, and website experience.
How do you perform technical SEO?
To start with, conduct a website technical SEO audit to find out the issues and potential areas of improvement which are affecting SEO. The audit will then help you figure out the SEO plan of action to improve your website’s SEO.
This plan generally includes fixing and reviewing every technical aspect of your website as per your needs including URL management, website architecture, site speed, sitemaps, link errors, implementing schema, mobile friendliness check, optimising metadata and more. We can use tools like Search Console, Google Analytics, AHREFS, Screaming frog and others to implement these fixes and validate optimisations.
What is the difference between technical and on-page SEO?
Technical SEO involves site audit and optimising the technical factors of your website like XML sitemaps, site structure, fixing broken links and indexing issues that affect your website’s SEO performance. While on-page SEO focuses rather on optimising the content of your website like text content, images, titles & meta descriptions and keyword usage. Most of the on-page optimisations do not require expert website development knowledge which technical optimisations may require.
Why is technical SEO important?
Technical SEO helps you set up the foundations of your website in the right way to ensure that search engines can understand and crawl your website. Not working on technical issues may result in difficulties for search engines to find and crawl your website to rank them in SERP. All in all, it helps search engines better understand & index pages and improve the overall website experience.
Is WordPress good for SEO?
Yes, WordPress is good for SEO. In fact, it is compatible and easy to use for websites looking to rank in search engine result pages. If you want to start working on SEO, WordPress can be the right platform for you.
WordPress is good for SEO as it has built-in SEO features, offers SEO-friendly WordPress themes & plugins, has a user-friendly interface that almost anyone can use and offers community support.
What does technical SEO include?
Technical SEO includes your overall SEO site audit and any technical edits that need to be done in order to help search engines find and index your website to rank in search results. They also play a part in improving website performance and user experience.
The scope of technical SEO can vary with website sizes and current SEO status. Sometimes, you may need to do a thorough technical audit of the entire site to find out problems in your website’s SEO performance while sometimes you may not need Some of the optimisation areas that technical SEO include is Site architecture, sitemap, indexing, URL issues (404/301/200), internal linking, hreflang setup, duplicate content, SSL certificates, site speed improvements, structured data and more.
How long does a technical SEO audit take?
Technical SEO audit might take anytime between 2-6 weeks depending on the size of your website. During the process, SEO professionals assess the existing situation of the technical website optimisations to create a site audit report which then helps to create SEO plans and strategies. The time also depends on how often you have been assessing your website’s SEO factors.
Is an SEO audit worth it?
Yes, an SEO audit is definitely worth it if you want to improve your SEO performance. An audit is a great way to discover technical, content, and off-site SEO issues that are preventing a website from ranking better in SERPs.
An SEO site audit can help you find out areas of improvement, new opportunities and competitive advantage areas. Addressing the website issues and working on these potential areas of improvement can then help a website increase its search engine visibility and attract more organic visitors.
What is a website SEO audit?
Website SEO audit unlike Technical SEO audit includes finding and analysing all of the aspects of the website that is contributing to SEO including technical, on-page and backlinks. The main goal of the website SEO audit is to find out and analyse the existing position & issues of the website to create an SEO strategy to improve the organic search traffic of the website.
A website SEO audit report is created after the audit, outlining the results and recommendations for increasing the website’s search engine exposure. The report can be used to create an SEO strategy that resolves the existing issues and also helps to improve organic search results performance.
Is there a limit to how many web pages Google bots can crawl or index?
Google uses a Crawl budget to determine how many pages it crawls and indexes for your website. If your website is large with more than 100,000 pages and when Google or any other search engine bots crawl your website in one go, your server usage will be maximum. So, search engines index and crawl pages while trying.
Ideally, you would want to minimise the crawl budget usage. It is the number of resources and time Google puts into crawling your website. The crawl budget is determined by how often search engine bots can crawl your site without causing issues to your website resources and how important crawling is.
